簡単な要約: 自動車の断熱は、単に「遮熱板を追加する」だけでは不十分です。信頼性の高い熱制御は、適切な材料、適切な間隔、そして振動や熱サイクルに耐える設置によって実現されます。このガイドでは、 排気管断熱材 、 ターボヒートシールド 、 触媒コンバーターのヒートシールド 、 吸気ヒートシールド 、そして一般的な 車のヒートシールド 設計ミス。
排気温度制御: 排気断熱ソリューション | 熱源の近くでのホース/ワイヤーの保護: ファイアスリーブ | ローカルバリアとエッジ保護: ヒートシールドテープ | 技術PDF: 技術文書をダウンロード
現代のパワートレインは、高温の部品を狭いスペースに詰め込んでいます。適切な 自動車断熱材 輻射熱やヒートソークにより、ボンネット下の温度が上昇し、ホースやワイヤーの寿命が短くなり、吸気温度が上昇し、プラスチックや複合材の近くにホットスポットが生じる可能性があります。適切な 自動車用ヒートシールド 戦略は次の 4 つの目標に焦点を当てています。
自動車の熱管理において、「ヒートシールド」は広い意味で使われることが多い。実際には、
深刻な地域では、最も信頼できるアプローチは 熱源を減らす その後 敏感な部品を保護する . まずは 排気断熱ソリューション 、必要に応じてターゲットシールドを使用します。
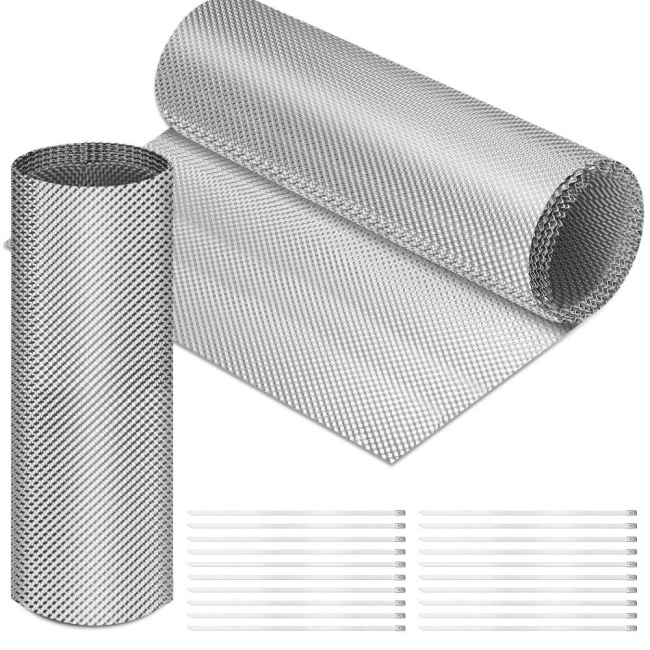
排気管断熱材 高温のパイプからの表面温度と放射熱を低減することを目的としています。特に、従来のスタンプ式シールでは対応できない狭い梱包エリアで効果的です。 車のヒートシールド 十分なエアギャップを維持できない。主な選定基準:
配管に高温部付近のホースや配線が含まれる場合は、次のような専用の保護を追加してください。 防火スリーブ 熱による老化を防ぎ、重要なポイントでのリスクを軽減します。
画像 #2
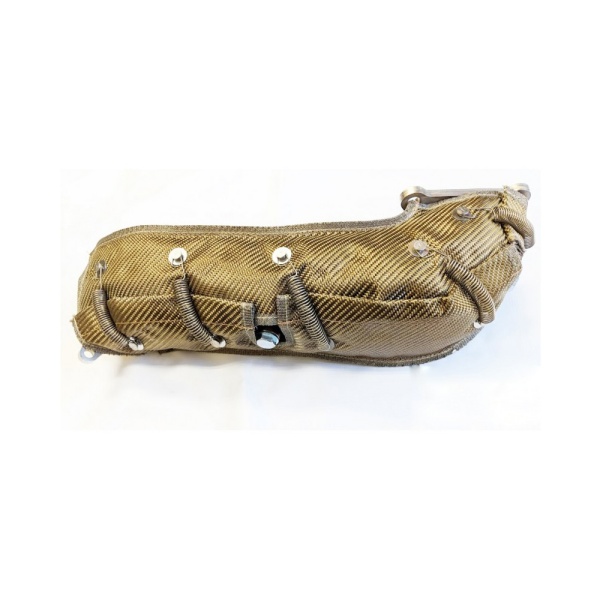

あ ターボヒートシールド エンジンベイ内で最も高い熱源の一つをターゲットとしています。信頼性の高いターボシールドには通常、以下の要件が求められます。
ターボ表面温度が極端に高い場合、シールドだけでは不十分な場合があります。シールドと以下の対策を組み合わせることを検討してください。 ソース断熱ソリューション 放射出力を低減し、周囲のコンポーネントの温度を安定させます。
あ 触媒コンバーターのヒートシールド アンダーボディ部品を保護し、床面、燃料ライン、周囲のプラスチック/トリム付近の熱曝露を低減するために一般的に使用されます。アンダーボディシールドは、水しぶき、塩分、破片の衝突、そして継続的な振動に耐える必要があります。ベストプラクティスは次のとおりです。
局所的なシーリングとエッジの補強については、必要に応じて検討してください。 遮熱テープとバリア 。
画像 #3
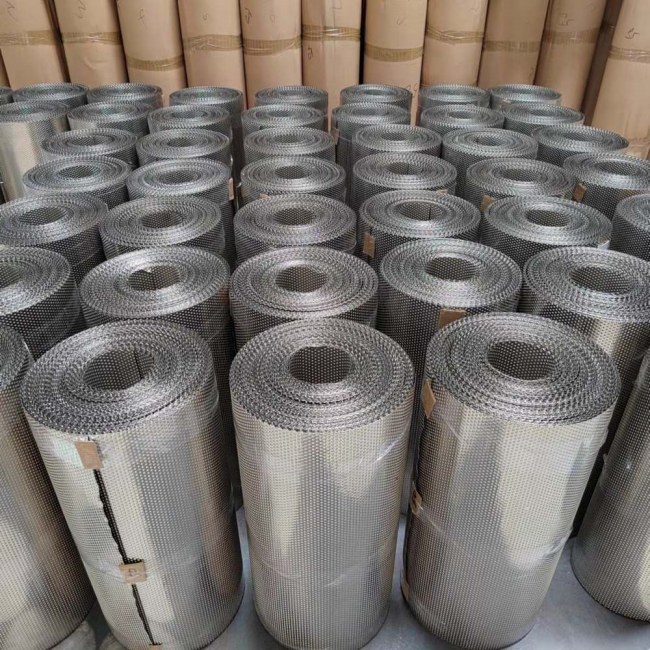

アン 吸気ヒートシールド 吸気経路を近くの熱源(排気マニホールド、ターボ、ラジエーター)から遮蔽することで、ヒートソークを低減し、吸気温度を安定させることに重点を置いています。保護性能だけでなく、より安定したパフォーマンスも目指しています。選定基準:
完全な熱戦略を構築する場合は、吸気シールドと排気側温度制御を組み合わせて、 排気断熱ソリューション 。
正確にはそうではありません。 自動車用ヒートシールド 放射熱を遮断し、隣接する部品を保護しながら、 排気管断熱材 熱源から熱を減少させます。猛暑地域では、通常、両方を組み合わせることで最も安定した結果が得られます。
あ ターボヒートシールド スペースを確保し、振動下でも安定し、より広範囲の排気熱設計と組み合わせることで、最も効果的です。非常に高い熱負荷の場合は、 ソース断熱ソリューション 。
専用のホースとケーブル保護具を使用してください。 防火スリーブ保護 配線が高温部品に近い場合。局所的なエッジ補強には、適切な 遮熱テープとバリア 該当する場合。
はい。多くの製品について、データシートと技術PDFを提供しています。 技術文書をダウンロード または、ドキュメントパックをリクエストしてください 見積もり依頼 。
車両プラットフォーム、熱源の位置(排気/ターボ/触媒/吸気)、クリアランス、取り付け方法、目標温度をお知らせください。実用的なヒートシールドと断熱材のご提案と、技術資料をご提供いたします。